
This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies. Some cells will deposit in the collagen tissue and will make a deposition there. Thickening of the lf is ascribed to buckling due to dsn. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. Uncertaintyexists as to whether this can occur without dsn.
Ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine is associated with facet joint degeneration: Affiliation 1 department of radiology, university of. But with pain and symptoms they can cause a narrowing of the spinal canal This condition is quite common for people who have chronic back pain. Uncertaintyexists as to whether this can occur without dsn. The ligametum flavin are thick yellow ligaments that add support for the spine.

Multilevel indicates that this is ha.
Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because. One of a series of bands of elastic tissue that runs between the lamina from the axis to the sacrum, the ligamentum flavum connects the laminae and fuses with the facet joint capsules. When the patient stands, causing straightening of the spine, the ligamentum flavum buckles and pushes in on the spinal nerves, resulting in pain to the lower extremities. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy (lfh) is mostly caused by mechanical stress and increased physical activity. Authors f h chokshi 1 , r m quencer, w r k smoker. Therefore we assume that it should kept in mind that lfh may develop at the adjacent level to the laminectomy and careful clinical and. An mri study the results of this study suggest that lf thickening may occur independently or could be associated with fjd especially on the ipsilateral side and this relationship is due to the vertebral level. They may thicken as we age or streets them. Ligamentum flavum thickening was measured on the axial image, perpendicular to the spinal canal axis and parallel to the lamina, where ligamentum flavum were seen along their entire length & measurement were taken at the half length of ligament flavum. It is a degenerative disease which involves the compression of nerves. presented a classification of the pathogenesis of the. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift arms and even paralysis.
Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because. When the patient stands, causing straightening of the spine, the ligamentum flavum buckles and pushes in on the spinal nerves, resulting in pain to the lower extremities. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a degenerative condition of the spine which most commonly occurs in theelderly where the tendons holding one vertebra to another thicken, decreasing the amount of room availablefor the spinal cord and the nerves that come off it. If you are not having symptoms then most leave them. Our primary hypothesis was that facet degenerativechanges alone, independent of dsn, can thicken the lf. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy (lfh) is mostly caused by mechanical stress and increased physical activity. Degenerative changes in posterior elements of the spine such as thickening or hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) may result in spinal stenosis. But with pain and symptoms they can cause a narrowing of the spinal canal
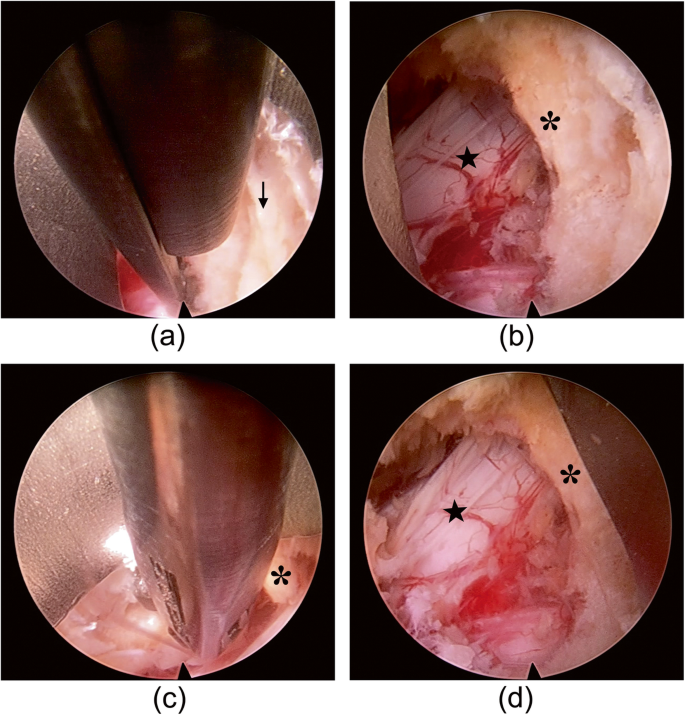
In a nutshell, this is what spinal ligaments called ligamentum flavum do.
But with pain and symptoms they can cause a narrowing of the spinal canal Ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine is associated with facet joint degeneration: An mri study the results of this study suggest that lf thickening may occur independently or could be associated with fjd especially on the ipsilateral side and this relationship is due to the vertebral level. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy means enlargement of the tough band of tissue that connects two bones of the spine. The thicker it becomes, the higher the risks of compressing the spinal cord or spinal nerves. Laminectomy cause thickening of ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. However, it is uncertain whether thickening can be present in the absence of dsn. Over time, these ligaments become thicker as they calcify or enlarge, which can have a noticeable effect on movement and other factors associated with the spine. Flavum is a latin word meaning yellow.
These bands serve as a covering over the spinal canal. Some cells will deposit in the collagen tissue and will make a deposition there. Thickening of the ligamentum flavum increases with age in the lower lumbar levels and in patients with chronic back pain. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy refers to abnormal thickening of the ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on the spine. Therefore we assume that it should kept in mind that lfh may develop at the adjacent level to the laminectomy and careful clinical and. However, it is uncertain whether thickening can be present in the absence of dsn.
Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift arms and even paralysis.
Degenerative changes in posterior elements of the spine such as thickening or hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) may result in spinal stenosis. With hypertrophy, ligamentum flavum (lf) increases in thickness (size). Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy which is also known by the name of ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological condition of the spine in which there is degeneration and swelling of the ligamentum flavum. Precise guided injections of the ligamentum flavum Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on the spine. Lf hypertrophy has been considered as a cause of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss). An mri study the results of this study suggest that lf thickening may occur independently or could be associated with fjd especially on the ipsilateral side and this relationship is due to the vertebral level. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc, prolapsed disc, extruded disc (or slipped disc) or protruded disc. The ligametum flavin are thick yellow ligaments that add support for the spine. Therefore we assume that it should kept in mind that lfh may develop at the adjacent level to the laminectomy and careful clinical and. Degenerative disc diseases and inflammatory changes can also. If you are not having symptoms then most leave them.
presented a classification of the pathogenesis of the ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy refers to abnormal thickening of the ligamentum flavum.

Thickening of the lf is ascribed to buckling due to dsn.

Ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine is associated with facet joint degeneration:

When the patient stands, causing straightening of the spine, the ligamentum flavum buckles and pushes in on the spinal nerves, resulting in pain to the lower extremities.

Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy means enlargement of the tough band of tissue that connects two bones of the spine.

Lf hypertrophy has been considered as a cause of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss).

These changes may cause the ligament to lose its elastic characteristics, which can result in buckling of the thickened ligamentum flavum into the vertebral canal or medial aspect of the ivf.

Two pathomechanisms have been proposed for the development of lf thickening:

These tough fibers connect spinal bones (vertebrae) together.

In a nutshell, this is what spinal ligaments called ligamentum flavum do.

With hypertrophy, ligamentum flavum (lf) increases in thickness (size).

If you are not having symptoms then most leave them.

Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also commonly known as ligamentum flavum thickening.

In this condition, the ligament attaching vertebrae together is stretched and bended and do not come to its original position even after relaxing.

Uncertaintyexists as to whether this can occur without dsn.

This deposition of the other cells is basically what we can call thickening of ligamentum flavum.

Ligamentum flavum thickening is a characteristic feature of lscs;

Is it buckling or enlargement?

It is frequently treated surgically, and it can recur.

If you are not having symptoms then most leave them.

Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy means enlargement of the tough band of tissue that connects two bones of the spine.

Lf hypertrophy has been considered as a cause of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss).

presented a classification of the pathogenesis of the.

Lf hypertrophy has been considered as a cause of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss).

This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum flava) which attach the individual vertebrae to one another, posterior to the central spinal canal.

This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum flava) which attach the individual vertebrae to one another, posterior to the central spinal canal.

Ligamentum flavum is an elastic ligament.

Degenerative changes in posterior elements of the spine such as thickening or hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) may result in spinal stenosis.

It is frequently treated surgically, and it can recur.

Precise guided injections of the ligamentum flavum

This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum flava) which attach the individual vertebrae to one another, posterior to the central spinal canal.

Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also commonly known as ligamentum flavum thickening.

Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably.

Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably.

Authors f h chokshi 1 , r m quencer, w r k smoker.

The thicker it becomes, the higher the risks of compressing the spinal cord or spinal nerves.

However, it is uncertain whether thickening can be present in the absence of dsn.